

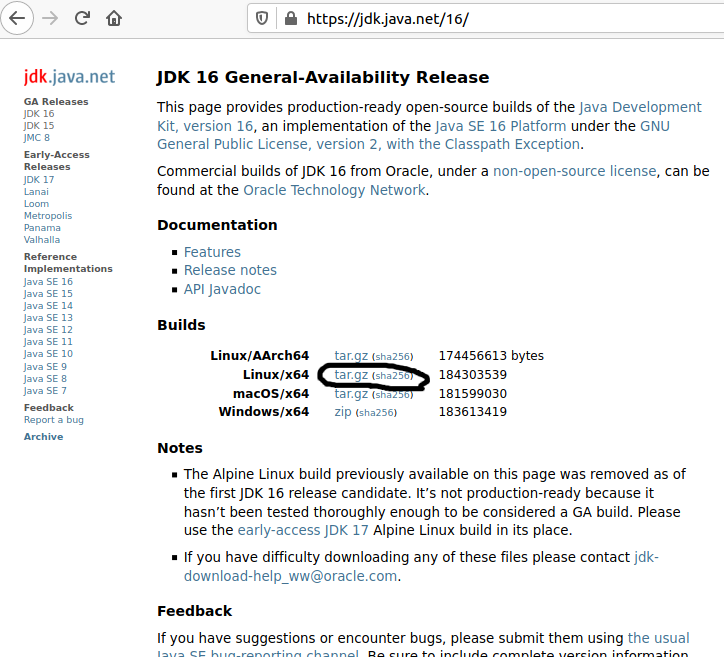
The Java SE 16 ( JSR 391) specification provides links to:Īnnex 1: The complete Java SE 16 API Specification.Īnnex 2: An annotated API specification showing the exact differences relative to Java SE 16. This page does not duplicate the descriptions provided by the Java SE 16 ( JSR 391) Platform Specification, which provides informative background for all specification changes and might also include the identification of removed or deprecated APIs and features not described here. In some cases, the descriptions provide links to additional detailed information about an issue or a change. These notes describe important changes, enhancements, removed APIs and features, deprecated APIs and features, and other information about JDK 16 and Java SE 16. Differences Between Oracle JDK and Oracle's OpenJDK.What's New in JDK 16 - New Features and Enhancements.If left unset, it is the same as setting it to true. When there is no security manager, there is no change to existing behavior the property can be set to true: =true or false. If a security manager is set, such as in WebStart applications, double-quotes are encoded as described. An argument containing double-quotes, other than first and last, is encoded to preserve the double-quotes when passed to the process previously, the embedded double-quotes would be dropped and not passed to the process. An empty argument is encoded as a pair of double-quotes ("") resulting in a zero length string passed for the argument to the process previously, it was silently ignored. An argument with a final trailing double-quote preceded by a backslash is encoded as a literal double-quote previously, the argument including the double-quote would be joined with the next argument.

Openjdk 16 jdk windows#
In the implementation on Windows, the system property =false ensures, for each argument, that double-quotes are properly encoded in the command string passed to Windows CreateProcess. ➜ Less Ambiguous Processing of ProcessBuilder Quotes on Windows By default, deserialization of java objects from the javaSerializedData attribute is allowed. To prevent deserialization of java objects from the attribute, the system property can be set to false value. The default value allows any object factory class specified in the reference to recreate the referenced object.Ĭom.trustSerialData: This system property allows control of the deserialization of java objects from the javaSerializedData LDAP attribute. This property applies both to the JNDI/RMI and the JNDI/LDAP built-in provider implementations. The filter property supports pattern-based filter syntax with the format specified by JEP 290. The factory class named by the reference instance is matched against this filter during remote reference reconstruction.
Openjdk 16 jdk serial#
: This system and security property allows a serial filter to be specified that controls the set of object factory classes permitted to instantiate objects from object references returned by naming/directory systems. ➜ New System and Security Properties to Control Reconstruction of Remote Objects by JDK's Built-in JNDI RMI and LDAP Implementations Users can, at their own risk, remove these restrictions by modifying the curity configuration file (or overriding it using the system property) and removing "SHA1 jdkCA & usage SignedJAR & denyAfter " from the security property and "SHA1 jdkCA & denyAfter " from the security property. These exceptions may be removed in a future JDK release. Any JAR signed with a SHA-1 certificate that does not chain back to a Root CA included by default in the JDK cacerts keystore will not be restricted.Any JAR signed with SHA-1 algorithms and timestamped prior to Januwill not be restricted.In order to reduce the compatibility risk for applications that have been previously timestamped or use private CAs, there are two exceptions to this policy:
Openjdk 16 jdk code#
It also applies to the signature and digest algorithms of the certificates in the certificate chain of the code signer and the Timestamp Authority, and any CRLs or OCSP responses that are used to verify if those certificates have been revoked. This applies to the algorithms used to digest, sign, and optionally timestamp the JAR. JARs signed with SHA-1 algorithms are now restricted by default and treated as if they were unsigned. Security-libs/curity ➜ Disable SHA-1 JARs


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
